REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Biology
4.4 Human Influences on the Environment
4.4.1 Understand the biological consequences of pollution of air by sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide
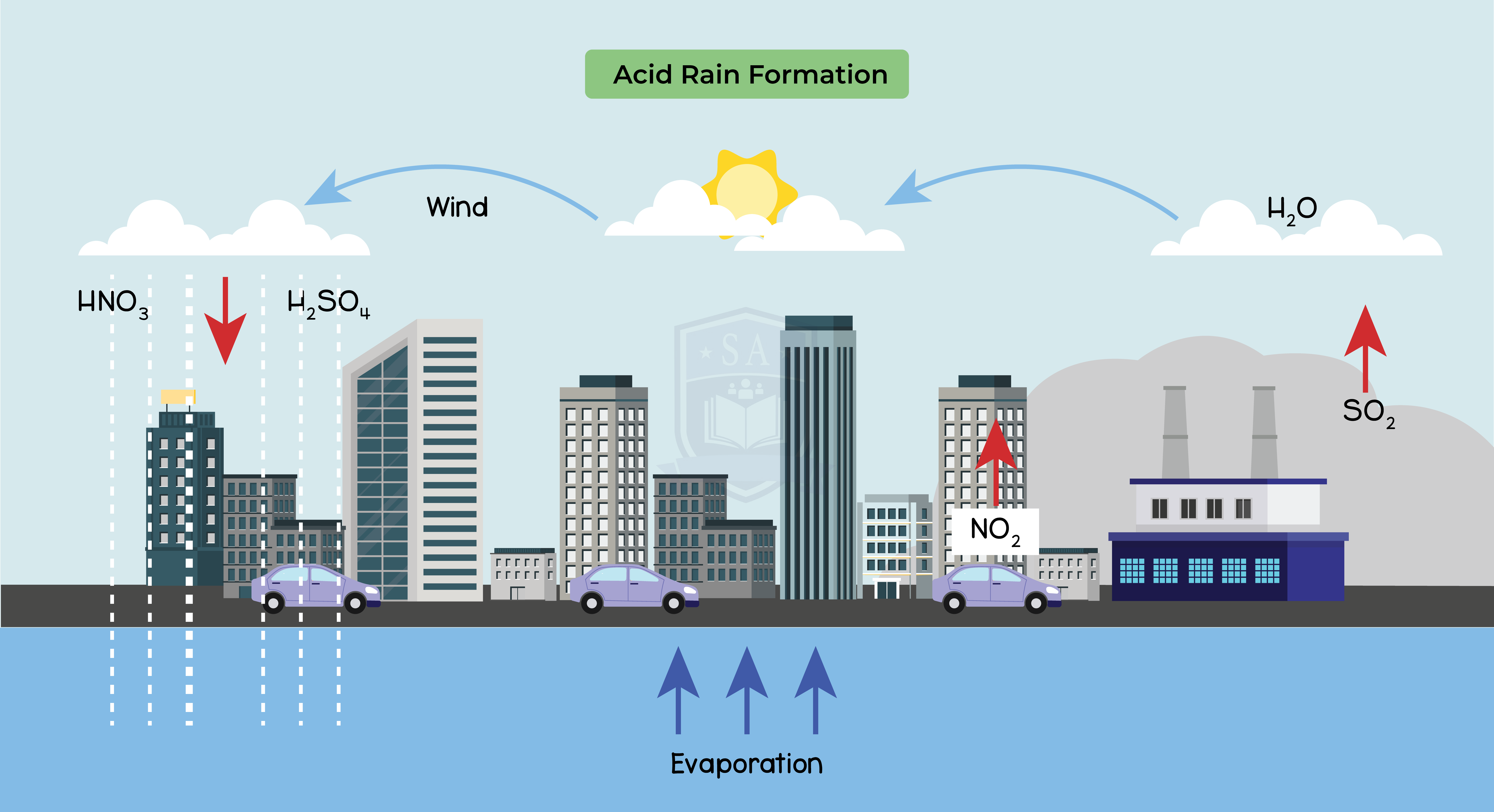
Sulphur dioxide:
- Produced by industrial processes
- Combustion of fossil fuels releases sulphur that reacts with oxygen to create oxides
- Sulphur dioxide dissolves in rainwater
- Produces dilute sulphuric acid
- Forms acid rain that:
- Damages plants
- Makes lakes too acidic to sustain aquatic life
- Can also lead to leaching of minerals such as aluminium into lakes
- Toxic to fish hence resulting in death of certain organisms
Carbon monoxide:
- Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels releases carbon monoxide
- Affects humans by binding to haemoglobin
- Irreversible binding
- Reduces oxygen carrying capacity of blood
- Leads to lower energy levels and slower growth
4.4.2 Understand that water vapour, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane and CFCs are greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases:
- Absorbs infrared radiation from the sun to trap it within the earth’s atmosphere
- If levels of greenhouses gases increase:
- Leads to the greenhouse effect
- Average temperature of the planet increases
- Greenhouse gases include:
- Water vapour
- Carbon dioxide
- Nitrous oxide
- Methane
- CFCs
4.4.3 Understand how human activities contribute to greenhouse gases
Human impact on greenhouse gases:
- Human activity has led to an increase in atmospheric levels of:
- CO2
- Methane
- CO2 is released through the combustion of fossil fuels
- Also released by deforestation and burning of plants
- Methane is released by agricultural practices
- Cattle release methane when bleaching during digestion
- Rice paddy fields are water logged encouraging the growth of methane releasing bacteria
4.4.4 Understand how an increase in greenhouse gases results in an enhanced greenhouse effect and that this may lead to global warming and its consequences
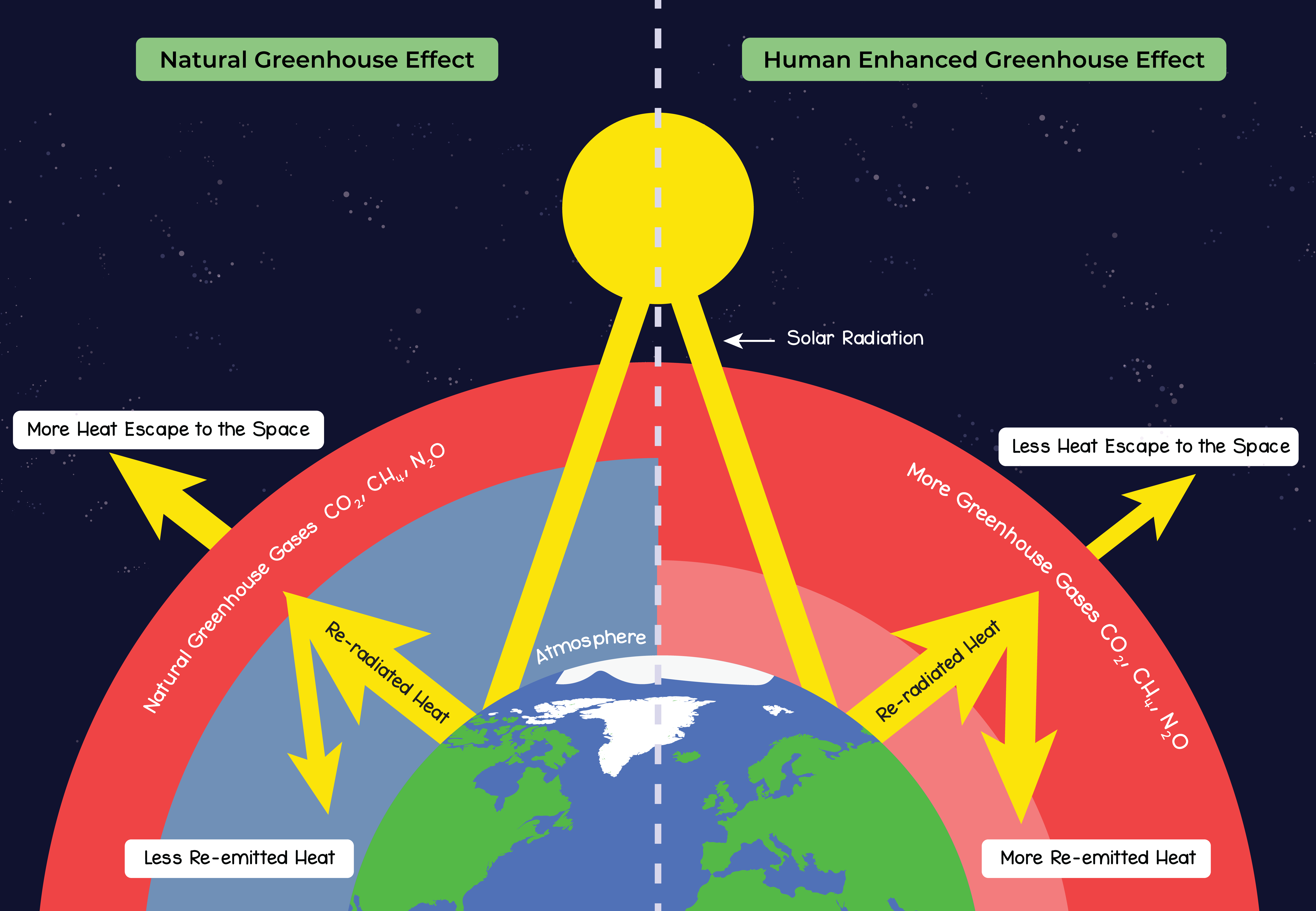
Greenhouse effect:
- UV rays from the sun enter the earth’s atmosphere
- Energy is absorbed by the earth’s surface and emitted back as heat
- Some of that heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases
- Heat is trapped in the atmosphere
- Enhanced greenhouse effect:
- Levels of greenhouse gases increase
- Increases average temperature of the earth above normal
- Leads to global warming
Consequences of global warming:
- Increasing ocean temperatures
- Causes polar ice caps to melt
- Increases sea levels and flooding in land nearby
- Rising temperatures
- Increases the chances of extreme weather conditions such as storms, floods and droughts
- Extreme weather conditions
- Lead to the change or loss of habitat for various animals
- Food chains are disrupted
- Biodiversity decreases
- Migration of many species increases
- They may be introduced to foreign land
- Spread uncommon diseases
- Disrupt food chains
4.4.5 Understand the biological consequences of pollution of water by sewage
Water pollution by toxic chemicals:
- Caused by:
- Toxic chemicals
- Untreated sewage
- Toxic chemicals:
- Found in pesticides and herbicides sprayed on plants to prevent crop damage
- Agricultural runoff when these chemicals are overused
- Chemicals cannot be broken down but can be absorbed by:
- Aquatic plants
- Animals
- Toxins build up in the organism over time
- At each level of the food chain, the chemical build up increases (bioaccumulation)
- Top predators have dangerously high toxin levels (biomagnification) leading to:
- Inability to reproduce
- Death
Water pollution by untreated sewage:
- Lack of sewage treatment leads to the runoff of sewage into water
- Is a food source for bacteria, decomposers and algae that can now reproduce rapidly
- Increase in population depletes the oxygen levels in water
- Threatens aquatic animals as they require oxygen to respire
- A complete lack of oxygen leads to the death of these aquatic animals
4.4.6 Understand the biological consequences of eutrophication caused by leached minerals from fertiliser
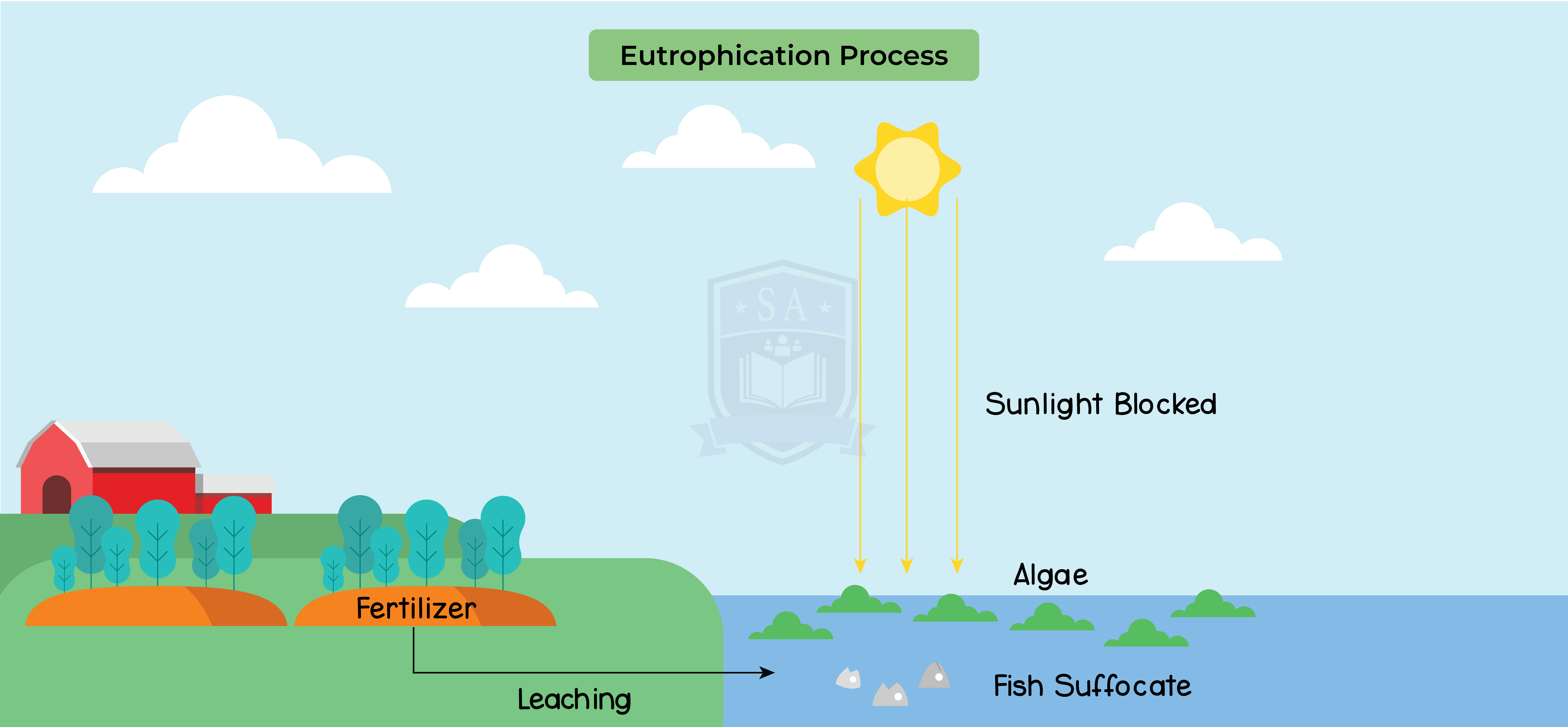
Eutrophication:
- Agricultural run off of fertilisers into surrounding water bodies
- Fertilisers provides algae and aquatic plants with the necessary nutrients for growth
- Leads to the significant increase in population of algae (algae bloom)
- Algal blooms blocks sunlight and compete for nutrients with aquatic plants
- Dead plants and algae provide bacteria with energy for growth
- Bacterial population also increases
- Bacteria compete for dissolved oxygen
- Eventually leading to the death of aquatic animals
4.4.7B Understand the effects of deforestation, including leaching, soil erosion, disturbance of evapotranspiration and the carbon cycle, and the balance of atmospheric gases

Deforestation:
- When trees are cut off or cleared from a large area of land
- Trees that are cleared for:
- Building
- Cattle farming
- Plantation of monocultures
- Decrease in population of trees causes severe habitat destruction for several species
- Can lead to extinction of species only found in particular environments e.g. rain forests
Soil erosion:
- Roots of a tree stabilise soil to prevent erosion
- Lack of trees leads to soil erosion
- Nutrients from the soil are leached away into rivers and lakes
- Loss of soil and nutrients is a permanent process
- Prevents the regrowth of a forest
Flooding:
- Trees hold topsoil together creating a barrier between land and water bodies
- The lack of topsoil and trees increase chances of:
- Flash floods
- Landslide
Increase in CO2 levels:
- Plants removes a significant amount of CO2 from the atmosphere for photosynthesis
- Decrease in population of trees leads to:
- Release of CO2 back into the atmosphere due to combustion
- Decrease in the overall amount of CO2 being absorbed
- This creates a net increase in CO2 levels in the atmosphere
Disruption of the water cycle:
- Plants or trees in large quantities release water through transpiration
- Water released can form clouds
- Leads to rainfall in surrounding land
Lack of trees prevent this process creating areas of drought

