REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry
2.5 Extraction and Uses of Metals
2.5.1C Know that most metals are extracted from ores found in the Earth’s crust and that unreactive metals are often found as the uncombined element
- The Earth’s crust contains metals and metal compounds such as gold, iron oxide and aluminium oxide
-
Reactive metals are often found chemically combined with other elements
- This is called ores
- Common examples of ores are haematite (iron ores) and bauxite (aluminium ores)
-
Unreactive metals are often found pure, as they are not chemically reactive
- They do not have to be extracted chemically
- This occurs as they do not easily react with other substances due to their chemical stability
- Examples include gold and platinum
2.5.2C Explain how the method of extraction of a metal is related to its position in the reactivity series, illustrated by carbon extraction for iron and electrolysis for aluminium
METHOD OF EXTRACTION
- The method of extraction of a metal depends on its position in the reactivity series
- If the metals are more reactive than carbon:
- They have to be extracted using electrolysis
- As they are too reactive and cannot be reduced by carbon
- If the metals are less reactive than carbon:
- They can be extracted by heating with carbon which reduces them

2.5.3C Be able to comment on a metal extraction process, given appropriate information
(detailed knowledge of the processes used in the extraction of a specific metal is not required)
EXTRACTION OF IRON
- Iron is below carbon in the reactivity series
- Heating with carbon would be more appropriate to extract iron from iron ore
- It is a cheap process as carbon is cheap and can be source of heat as well
EXTRACTION OF ALUMINUIM
- Aluminium is more reactive than carbon according to the reactivity series
- Electrolysis should be used to extract aluminium from aluminium ore
- Large amount of electricity required, so it is a relatively expensive process
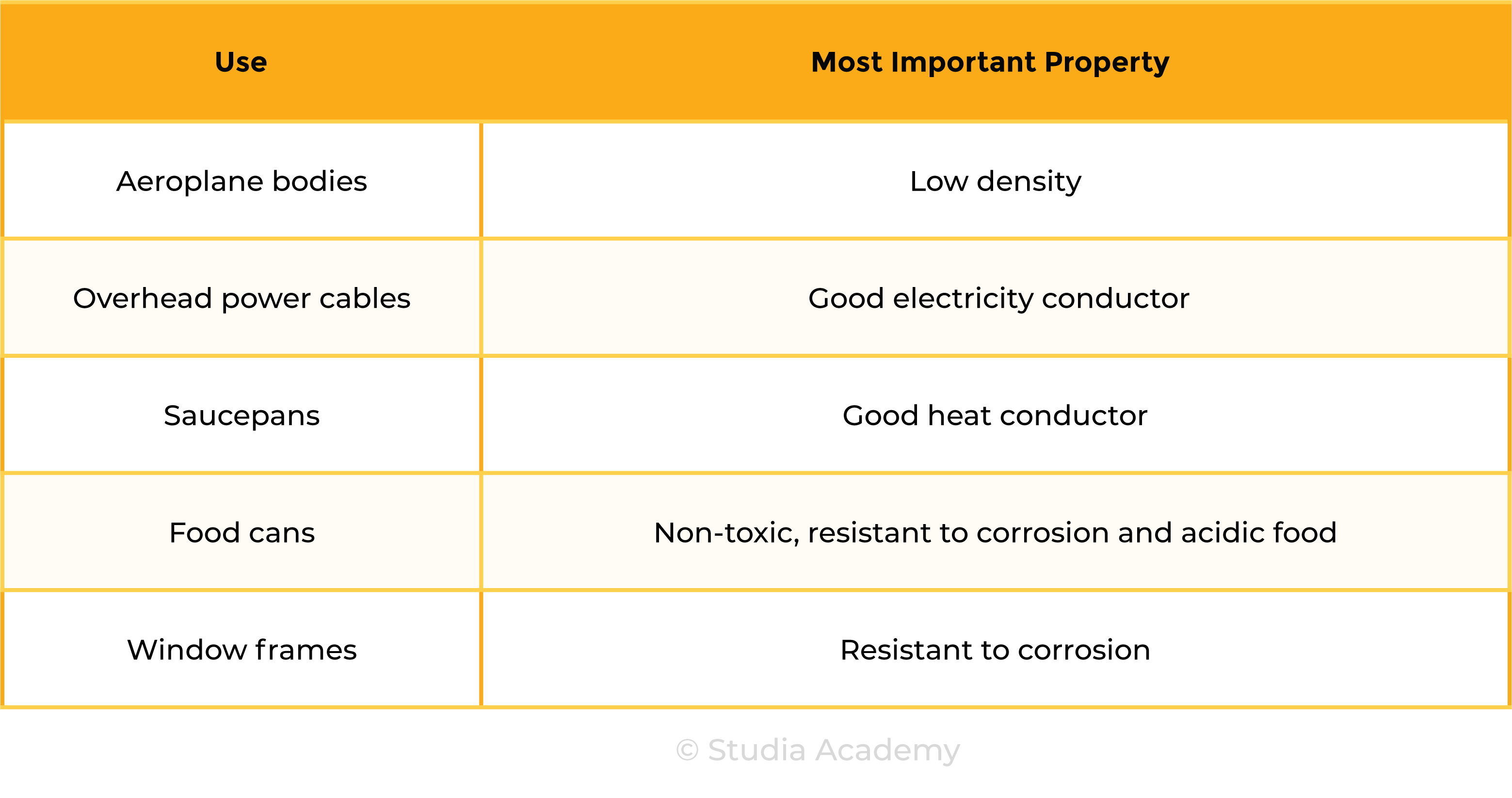
2.5.4C Explain the uses of aluminium, copper, iron and steel in terms of their properties
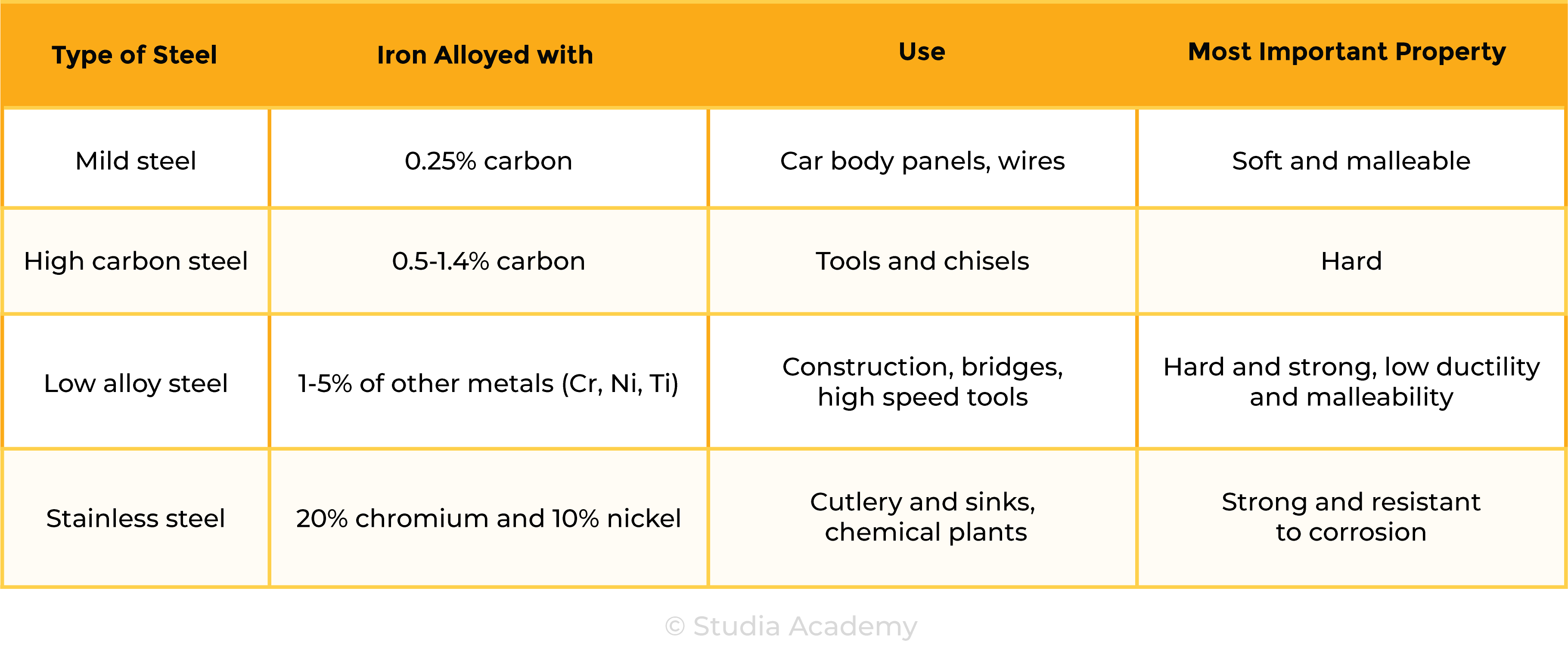
the types of steel will be limited to low-carbon (mild), high-carbon and stainless
Uses of Aluminium
Uses of Copper

Uses of Iron
Uses of Steel
2.5.5C Know that an alloy is a mixture of a metal and one or more elements, usually other metals or carbon
ALLOYS
- Definition: mixture of a metal and one or more elements, usually other metals or carbon
- They are mixed together physically, but not chemically combined
- Alloys have properties that are different from pure metals
- Greater strength
- Hardness
- Resistance to corrosion
- Resistance to extreme temperatures
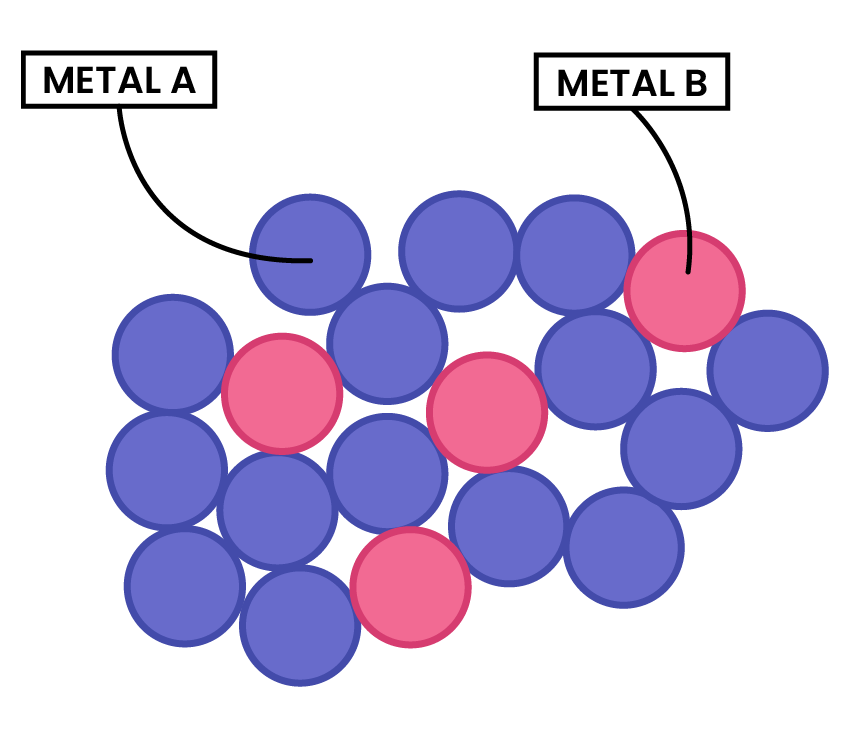
2.5.6C Explain why alloys are harder than pure metals
PROPERTIES OF ALLOYS
- Alloys contain metal ions of different sizes, which distorts the regular arrangement of metal ions
- This makes it more difficult for the layers to slide over each other
- Thus, alloys are harder than pure metals
- Examples of alloys include:
- Brass (copper + zinc)
- Steel (iron + other elements)