REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry
4.1 Introduction
4.1.1 Know that a hydrocarbon is a compound of hydrogen and carbon only
Hydrocarbon is a compound containing hydrogen and carbon only.
4.1.2 Understand how to represent organic molecules using empirical formulae, molecular formulae, general formulae, structural formulae and displayed formulae
- Empirical formula shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms
- Molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms
- General formula shows a ratio of atoms in a family of compounds in terms of ‘n’ where n is a varying whole number
- Simplified Structural formula shows the way in which atoms are bonded (Structure), but not all bonds
- Displayed Structural formula shows all atoms and bonds in a molecule
4.1.3 Know what is meant by the terms homologous series, functional group and isomerism
HOMOLOGOUS SERIES
- Series of compounds with:
- Same functional group
- Same general formula
- Similar chemical properties
- Gradually increasing physical properties along the series (e.g. boiling point)
FUNCTIONAL GROUP
- A group of atoms present in the compound
- It is a distinctive combination of atoms in the compound
- It is responsible for the chemical reactions of a compound
ISOMERISM
- Compounds with:
- Same molecular formula
- But different structural formula
- Due to different arrangements of atoms
More will be discussed throughout this topic.
4.1.4 Understand how to name compounds relevant to this specification using the rules of international Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature students will be expected to name compounds containing up to six carbon atoms
PREFIXES (BEGINNING OF THE NAME)
- Depends on the number of carbons in the parent chain – parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain
- 1C – Meth
- 2C – Eth
- 3C – Prop
- 4C – But
- 5C – Pent
- 6C – Hex
SUFFIXES
- Refers to the functional group
- Alkanes – ane
- Alkenes – ene
- Alcohol – ol
- Carboxylic acids – anoic acid
- Esters – yl, anoate
4.1.5 Understand how to write the possible structural and displayed formulae of an organic molecule given its molecular formula
If the molecular formula given is C2H6:
- Structural formula: CH3CH3
- Displayed formula:
Be aware of isomers
- Different structural formula and displayed formula can be drawn from same molecular formula
Example: C5H12
To name the alkane isomers:
Consider the number of carbons in the longest continuous carbon chain.
Know that the CH3 group is called the “methyl” group .
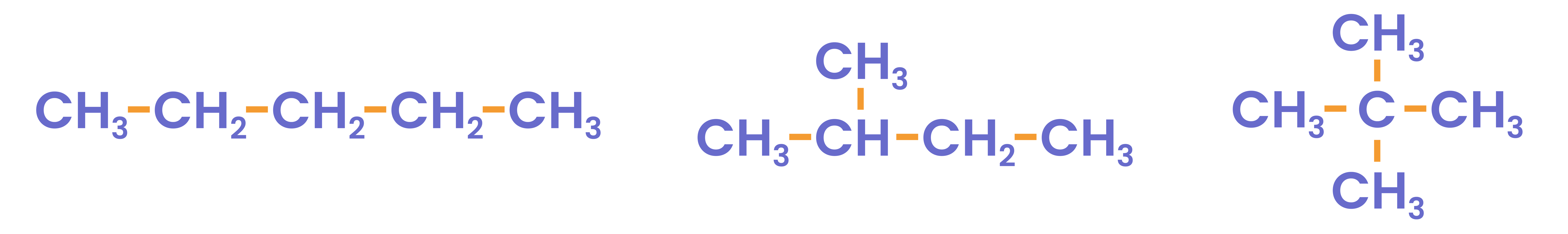
4.1.6 understand how to classify reactions of organic compounds as substitution, addition and combustion
Knowledge of reaction mechanisms is not required
ADDITION REACTIONS
- Involve only one product
- 2 reactants → 1 product
- E.g. ethene + hydrogen → ethane
SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
- Involve two products
- 2 reactants → 2 products
- Hydrogen chloride + ethanol → chloroethane + water
(Cl replaces OH, they swap places)
COMBUSTION REACTIONS
- Involves the reaction of a fuel with oxygen
- Complete combustion of hydrocarbon produces water and carbon dioxide
- Incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon produces water and carbon monoxide

