REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry
4.3 Alkanes
4.3.1 Know the general formula for alkanes
General formula for alkanes:
CnH2n+2
EXAMPLE
Ethane is a type of alkane with the formula C2H6
4.3.2 Explain why alkanes are classified as saturated hydrocarbons
ALKANES
- Contain only single bonds (C–C and C–H)
- Each carbon has 4 single bonds around it, which is the maximum number of bonds it can form
- Therefore, the carbons are saturated
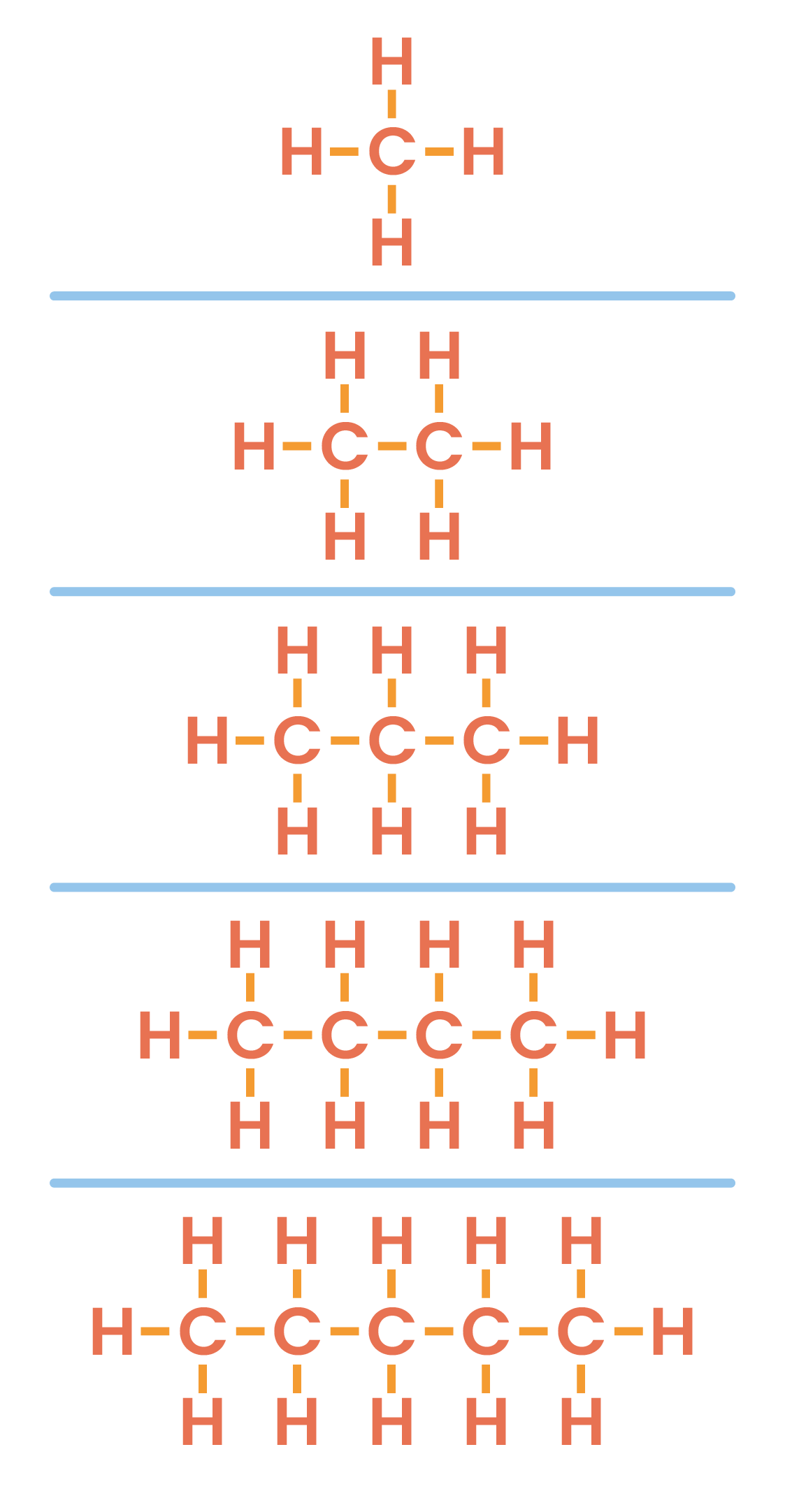
4.3.3 Understand how to draw the structural and displayed formulae for alkanes with up to five carbon atoms in the molecule, and to name the unbranched-chain isomers
4.3.4 Describe the reactions of alkanes with halogens in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, limited to mono-substitution
knowledge of reaction mechanisms is not required
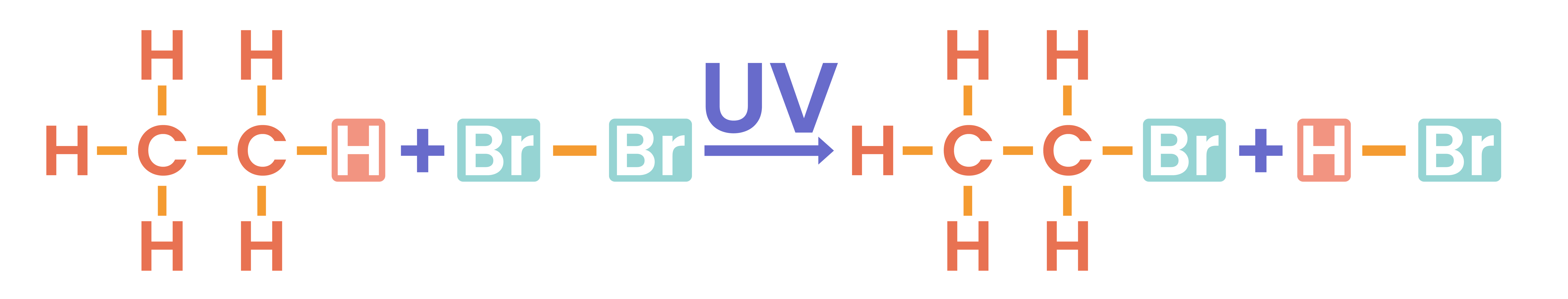
Reaction of Alkanes with Halogens
UV
alkane + halogen → halogenoalkane + hydrogen halide
- As alkanes are saturated, they undergo substitution reaction
- The reaction only happens in presence of ultraviolet (UV) radiation
- It is a mono-substitution reaction:
- One of the hydrogen is substituted by the halogen
Product names:
fluoro / chloro / bromo / iodo [alkane name]
fluoro / chloro / bromo / iodo [alkane name]
+ hydrogen fluoride / chloride / bromide / iodide
UV
C2H6 + Br2 → C2H5Br + HBr