REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry
4.5 Alcohols
4.5.1C Know that alcohols contain the functional group −OH
The functional group of alcohol is -OH
– O – H
4.5.2C Understand how to draw structural and displayed formulae for methanol, ethanol, propanol (propan-1-ol only) and butanol (butan-1-ol only), and name each compound
the names propanol and butanol are acceptable
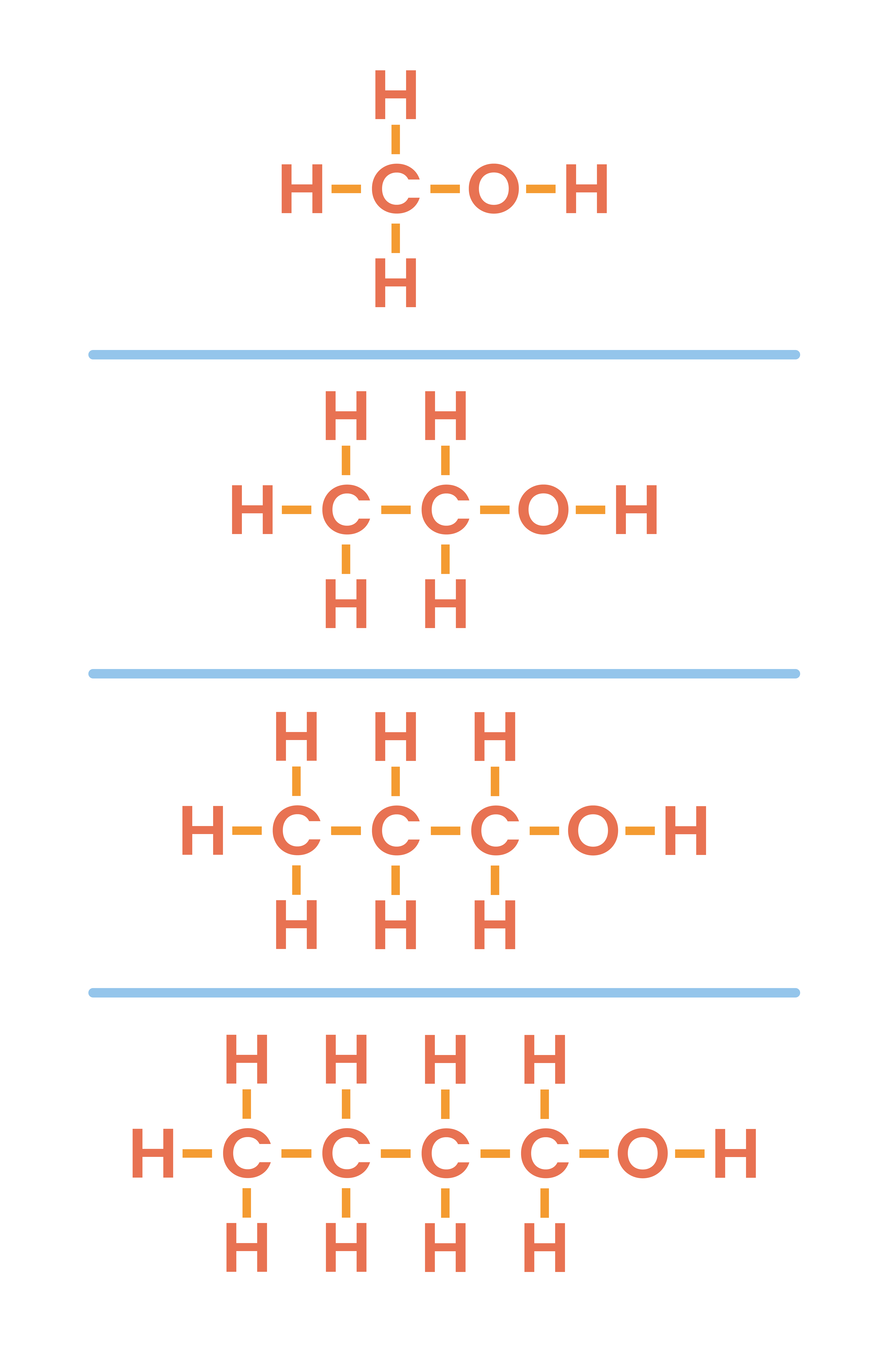
4.5.3C Know that ethanol can be oxidised by:
- Burning in air or oxygen (complete combustion)
- Reaction with oxygen in the air to form ethanoic acid (microbial oxidation)
- Heating with potassium dichromate(VI) in dilute sulfuric acid to form ethanoic acid
OXIDATION OF ETHANOL
- Ethanol undergoes oxidation in three different ways
1. Complete combustion
- Burning in air or oxygen
2. Microbial oxidation
3. Ethanol and potassium dichromate(VI)
- With heat
- With dilute sulfuric acid
4.5.4C Know that ethanol can be manufactured by:
- Reacting ethene with steam in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst
- At a temperature of about 300oC and a pressure of about 60–70 atm
- The fermentation of glucose, in the absence of air, at an optimum temperature of about 30oC and using the enzymes in yeast
Manufacture of Ethanol
1. Ethene + steam
- Catalyst: phosphoric acid
Temperature: 300oC
Pressure: 60-70 atm
Features
- Continuous process
- Produces very pure ethanol
- Comes from non-renewable sources, ethene extracted from crude oil
2. Fermentation of glucose
- Absence of air (anaerobic)
- Optimum temperature of about 30oC
- Using the enzymes in yeast
Features
- Batch process
- Produces impure ethanol, so must be distilled
- Comes from renewable sources such as glucose from plants
4.5.5C Understand the reasons for fermentation, in the absence of air, and at an optimum temperature
Fermentation of Glucose
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
- Why is the optimum temperature around 25 to 50oC?
- If too low: yeast that is used would be inactive
- If too high: enzymes in yeast would be denatured / would no longer function
- Why must air be kept out (absence of oxygen)?
- If there is air: ethanol would be oxidised to ethanoic acid

